Engine
How does it work?

An engine is a machine designed and built to convert heat energy to mechanical by burning fuel such as gasoline. In automotive, an engine is the heart of the vehicle that produces power to move the vehicle. It is one of the major component in the vehicle that requires maintenance and care.
Today's modern vehicles use internal combustion engines, which injects gas fuel such as gasoline to run the engine. This type of engine has been used as early as 1800s, mass produced by Henry Ford's Ford Motor Company, as a replacement of steam engines.
An engine is a very sophisticated machine that requires a lot of care. If you read the vehicle owner's manual, you can find out that there is a maintenance section that provides list of services required based on the vehicle's mileage or age.
Tip: The more you try to understand the vehicle, the longer your vehicle can be operated without breaking apart. Also, make sure to change your vehicle's engine oil and filters in time.
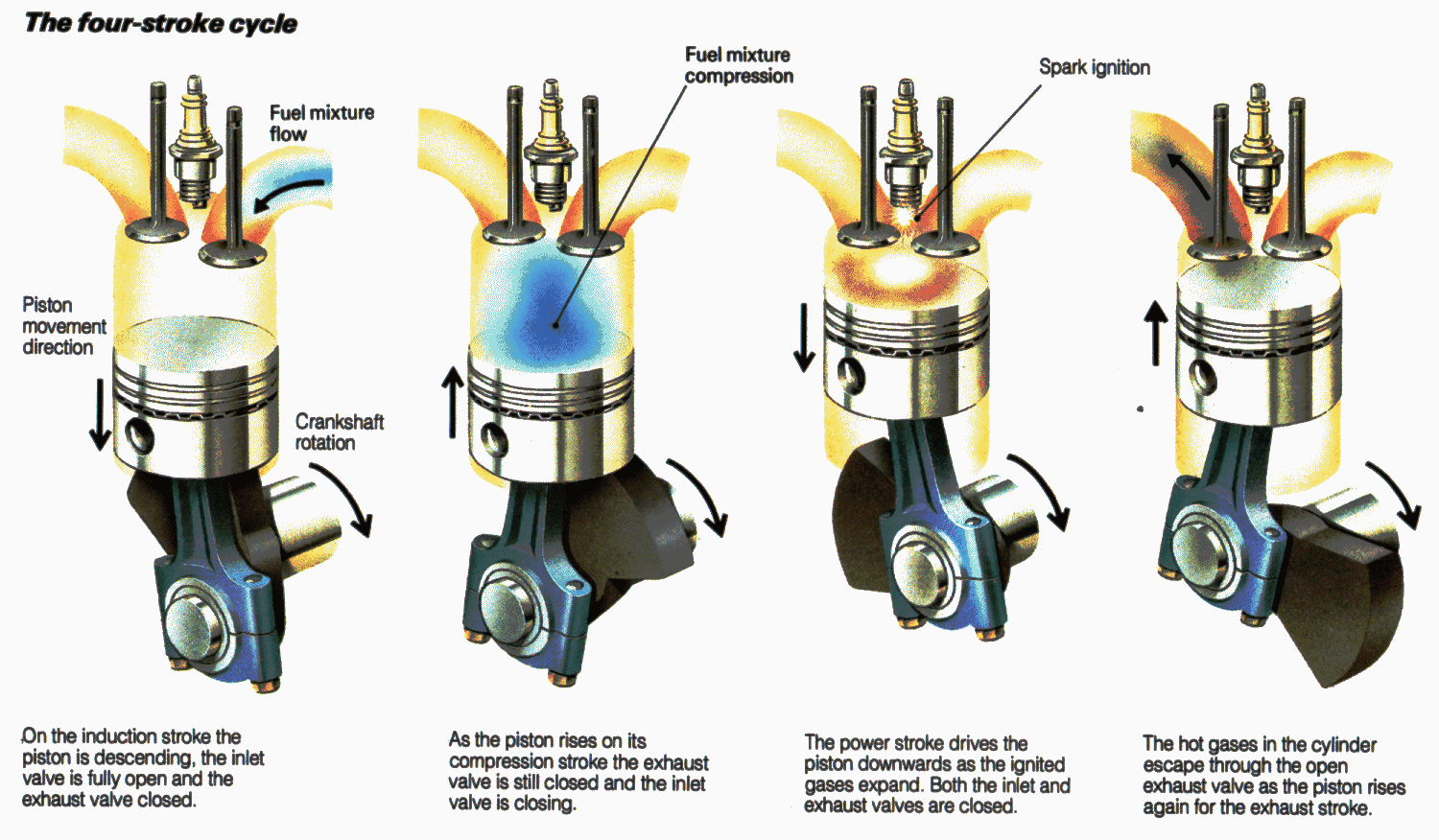
When the vehicle is turned on, the car battery supplies electricity to the starting motor, which rotates the flywheel to rotate engine's cranks, pistons, and vales. The vehicle's mechanical energy is created when this rotation happens. By understanding the four-stroke combustion engine cycle, you will understand how engine converts heat energy into mechanical energy.
Four-stroke combustion cycle is a cycle used to convert heat energy into mechanical energy. During this cycle, the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. Each strokes has different task to convert energy, and must be completed in the correct order. Plus, depends on the fuel type, the order may change. The gasoline engine requires the following steps to happen in a correct order.